When considering your investing strategy, taxes may be competing with market volatility and inflation for your attention, but it's still important to understand what you are paying and how it affects the overall growth of your portfolio. There may be ways to structure your investments in a more tax-savvy way.
"We all have to pay our tax bills, but we don't need to leave a tip," says Michelle Howell, a vice president and financial consultant at a Fidelity Investments Center based in Edina, Minnesota.
Tallying up what taxes you pay on your investments and why is not an easy task—it involves a lot of paperwork and digging through tax statements. In any given year, you might incur income taxes on interest, dividends, and realized gains on investments. The rates you pay depend on various factors, which will be specific to your financial holdings and your overall income.
It can be important to think about whether you are invested in the right accounts, because tax-smart asset location can potentially help improve after-tax returns. But often investors end up with tax-inefficient investments nonetheless, and it can affect their portfolio's overall performance.
Whether you work with a professional to build a more tax-savvy investment plan or try a DIY approach, here’s how to get started.
1. Check your accounts
The first thing to do is see if you have your money in the right accounts for your goals, starting with tax-deferred ones like 401(k) plan accounts and traditional IRAs and then thinking about a Roth IRA, 529 college savings account, or a health savings account (HSA), where the growth is potentially tax-free, says Andrew Bachman, director of tax and retirement income solutions at Fidelity.
Next look at what holdings you have in your taxable investment accounts and how much tax you are paying on the dividend and interest income they are generating during the year. Some securities may also pass along capital gains. You may see holdings that are generating more in taxes than other positions.
For instance, Howell had a client with a nest egg of around $1 million whose tax issue centered around one large position in a particular investment. Over a one-year period, the distributions from the one investment resulted in approximately $70,000 in federal taxes and the client was concerned about the tax-efficiency of that position in their portfolio.
Note that selling investments in a taxable account produces potential tax consequences too, either with capital gains or capital losses. Even the common practice of reinvesting your dividends and interest income doesn’t change the tax implications of receiving those distributions, because you’ll generally still have to pay tax on what you've earned in a taxable account.
You can get all the information you need to assess your portfolio's tax burden from reporting documents like 1099 forms from your account custodian. "But most people don't do it because it’s difficult," says Bachman.
Because these types of assessments are complicated, you should consult with a financial professional to assess your specific situation. They may have software that can help crunch the numbers.
2. Develop a transition plan
The strategy question is: What do you do with the observations once you know what tax you are paying and why?
To change things up with your taxable accounts, you don't necessarily have to sell a position completely, potentially generating capital gains. Howell says instead you can do something as simple as stop reinvesting dividends or interest income from an investment and start putting that money into more tax-efficient investments. One option might include your own state’s municipal bonds, which in many cases would be both federal- and state-income-tax-free. Don't let taxes drive your decision making entirely, however: make sure whatever tax-efficient alternative you choose makes sense from an investment perspective first.
If you decide to make changes, you don’t want to just dump all your current holdings and start over from scratch with other investments. The order of operations becomes key to tax management.
"It can be important to use as many of your existing suitable positions as possible, while adding additional tax-efficient positions," says Howell.
Howell's client with the large tax bill decided to work on shifting to a more tax-efficient position over time. The strategy that they chose for their own needs and goals focused more on buying individual securities. That strategy might not be the best for everyone, as the vast majority of individual investors might not want to assemble a portfolio of individual securities and manage it closely.
3. Keep an eye on things
Ongoing maintenance is key. Restructuring your portfolio for tax-efficiency is not a one-shot deal. You need a plan going forward, and you might want to shift your positions throughout the year with tax-loss harvesting to try to offset your gains with losses by strategically selling investments.
Be mindful, however, of the IRS wash sale rules that can disallow a loss if you buy the same or substantially identical security within the restricted window.
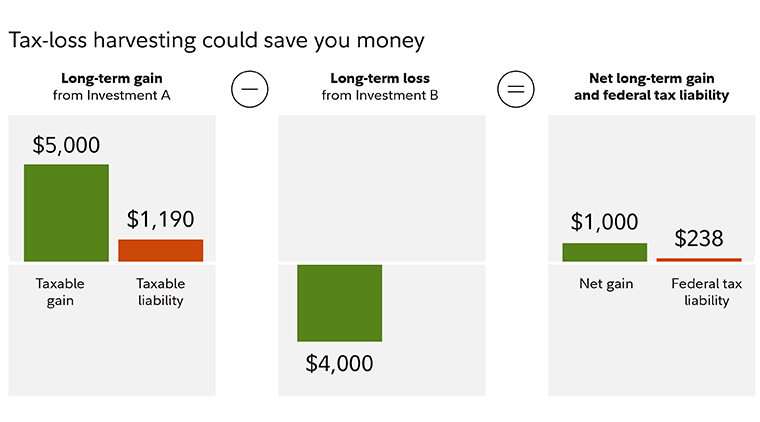
This is how it worked for another of Howell’s clients, who had about $1.5 million in taxable investment accounts. They had been paying about $11,000 a year in federal taxes, and wanted to see if they could reduce that amount with a different mix of assets. After running the numbers, they came up with a plan to shift to a particular set of investments. After that, the goal was to reduce future tax drag by managing the new positions with ongoing tax-loss harvesting.
Tip: See the potential impact of tax-smart investing over time.
4. Think long-term
If your long-term plans include giving away your assets, you might want to consider other structures that will allow the money to grow tax-free to manage the tax impact to both yourself and your beneficiaries. There are certain types of trusts and estate-planning strategies you can consider, and also various charitable giving options.
Bottom line
Every tax situation is different, so you want a strategy that meets your needs and that you have the ability to maintain. Tax strategies are particularly complex, so you may want to consult with a financial professional to assess your specific situation and help you set the right course.


