Goal
To profit from neutral stock price action near the strike price of the short puts (center strike) with limited risk.
Explanation
A long butterfly spread with puts is a three-part strategy that is created by buying one put at a higher strike price, selling two puts with a lower strike price and buying one put with an even lower strike price. All puts have the same expiration date, and the strike prices are equidistant. In the example one 105 Put is purchased, two 100 Puts are sold and one 95 Put is purchased. This strategy is established for a net debit, and both the profit potential and risk are limited. The maximum profit is realized if the stock price is equal to the strike price of the short puts (center strike) on the expiration date. The maximum risk is the net cost of the strategy including commissions and is realized if the stock price is above the higher strike price or below the lower strike price at expiration.
This is an advanced strategy because the profit potential is small in dollar terms and because “costs” are high. Given that there are three strike prices, there are multiple commissions in addition to three bid-ask spreads when opening the position and again when closing it. As a result, it is essential to open and close the position at “good prices.” It is important to ensure the risk/reward ratio including commissions is favorable or acceptable.
Example of long butterfly spread with puts
| Buy 1 XYZ 105 put at 6.25 | (6.25) |
| Sell 2 XYZ 100 puts at 3.15 | 6.30 |
| Buy 1 XYZ 95 put at 1.25 | (1.25) |
| Net cost = | (1.20) |
Maximum profit
The maximum profit is equal to the difference between the highest and center strike prices less the net cost of the position including commissions, and this profit is realized if the stock price is equal to the strike price of the short puts (center strike) at expiration.
In the example above, the difference between the highest and center strike prices is 5.00, and the net cost of the strategy is 1.20, not including commissions. The maximum profit, therefore, is 3.80 less commissions.
Maximum risk
The maximum risk is the net cost of the strategy including commissions, and there are two possible outcomes in which a loss of this amount is realized. If the stock price is above the highest strike price at expiration, then all puts expire worthless and the full cost of the strategy including commissions is lost. Also, if the stock price is below the lowest strike price at expiration, then all puts are in the money and the butterfly spread position has a net value of zero at expiration. As a result, the full cost of the position, 1.20, including commissions is lost.
Breakeven stock price at expiration
There are two breakeven points. The upper breakeven point is the stock price equal to the highest strike price minus the cost of the position including commissions. The lower breakeven point is the stock price equal to the lowest strike price plus the cost of the position including commissions.
Profit/Loss diagram and table: long butterfly spread with puts
| Buy 1 XYZ 105 put at 6.25 | (6.25) |
| Sell 2 XYZ 100 puts at 3.15 | 6.30 |
| Buy 1 XYZ 95 put at 1.25 | (1.25) |
| Net cost = | (1.20) |
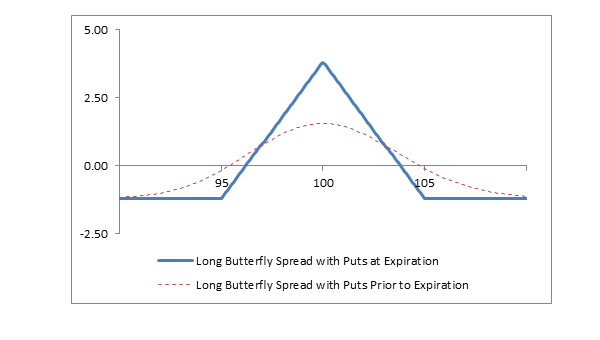
| Stock Price at Expiration | Long 1 105 Put Profit/(Loss) at Expiration | Short 2 100 Puts Profit/(Loss) at Expiration | Long 1 95 Put Profit/(Loss) At Expiration | Net Profit/(Loss) at Expiration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 110 | (6.25) | +6.30 | (1.25) | (1.20) |
| 105 | (6.25) | +6.30 | (1.25) | (1.20) |
| 100 | (1.25) | +6.30 | (1.25) | +3.80 |
| 95 | +3.75 | (3.70) | (1.25) | (1.20) |
| 90 | +8.75 | (13.70) | +3.75 | (1.20) |
Appropriate market forecast
A long butterfly spread with puts realizes its maximum profit if the stock price equals the center strike price on the expiration date. The forecast, therefore, can either be “neutral” or “modestly bearish,” depending on the relationship of the stock price to the center strike price when the position is established.
If the stock price is at or near the center strike price when the position is established, then the forecast must be for unchanged, or neutral, price action.
If the stock price is above the center strike price when the position is established, then the forecast must be for the stock price to fall to the center strike price at expiration (modestly bearish).
While one can imagine a scenario in which the stock price is below the center strike price and a long butterfly spread with puts would profit from bullish stock price action, it is most likely that another strategy would be a more profitable choice for a bullish forecast.
Strategy discussion
A long butterfly spread with puts is the strategy of choice when the forecast is for stock price action near the center strike price of the spread, because long butterfly spreads profit from time decay. However, unlike a short straddle or short strangle, the potential risk of a long butterfly spread is limited. The tradeoff is that a long butterfly spread has a much lower profit potential in dollar terms than a comparable short straddle or short strangle. Also, the commissions for a butterfly spread are higher than for a straddle or strangle.
Long butterfly spreads are sensitive to changes in volatility (see Impact of Change in Volatility). The net price of a butterfly spread falls when volatility rises and rises when volatility falls. Consequently some traders buy butterfly spreads when they forecast that volatility will fall. Since the volatility in option prices tends to fall sharply after earnings reports, some traders will buy a butterfly spread immediately before the report. The potential profit is “high” in percentage terms and risk is limited to the cost of the position including commissions. Success of this approach to buying butterfly spreads requires that the stock price stay between the lower and upper strike prices of the butterfly. If the stock price rises or falls too much, then a loss will be incurred.
If volatility is constant, long butterfly spreads with puts do not rise in value and, therefore, do not show much of a profit, until it is very close to expiration and the stock price is close to the center strike price. In contrast, short straddles and short strangles begin to show at least some profit early in the expiration cycle as long as the stock price does not move out of the profit range.
Furthermore, while the potential profit of a long butterfly spread is a “high percentage profit on the capital at risk,” the typical dollar cost of one butterfly spread is “low.” As a result, it is often necessary to trade a large number of butterfly spreads if the goal is to earn a profit in dollars equal to the hoped-for dollar profit from a short straddle or strangle. Also, one should not forget that the risk of a long butterfly spread is still 100% of the cost of the position. Therefore, if the stock price begins to fall below the lowest strike price or to rise above the highest strike price, a trader must be ready to close out the position before a large percentage loss is incurred.
Patience and trading discipline are required when trading long butterfly spreads. Patience is required because this strategy profits from time decay, and stock price action can be unsettling as it rises and falls around the center strike price as expiration approaches. Trading discipline is required, because, as expiration approaches, “small” changes in stock price can have a high percentage impact on the price of a butterfly spread. Traders must, therefore, be disciplined in taking partial profits if possible and also in taking “small” losses before the losses become “big.”
Impact of stock price change
“Delta” estimates how much a position will change in price as the stock price changes. Long puts have negative deltas, and short puts have positive deltas.
Regardless of time to expiration and regardless of stock price, the net delta of a long butterfly spread remains close to zero until one or two days before expiration. If the stock price is above the highest strike price in a long butterfly spread with puts, then the net delta is slightly negative. If the stock price is below the lowest strike price, then the net delta is slightly positive. Overall, a long butterfly spread with puts does not profit from stock price change; it profits from time decay as long as the stock price is between the lowest and highest strikes.
Impact of change in volatility
Volatility is a measure of how much a stock price fluctuates in percentage terms, and volatility is a factor in option prices. As volatility rises, option prices tend to rise if other factors such as stock price and time to expiration remain constant. Long options, therefore, rise in price and make money when volatility rises, and short options rise in price and lose money when volatility rises. When volatility falls, the opposite happens; long options lose money and short options make money. “Vega” is a measure of how much changing volatility affects the net price of a position.
Long butterfly spreads with puts have a negative vega. This means that the price of a long butterfly spread falls when volatility rises (and the spread loses money). When volatility falls, the price of a long butterfly spread rises (and the spread makes money). Long butterfly spreads, therefore, should be purchased when volatility is “high” and forecast to decline.
Impact of time
The time value portion of an option’s total price decreases as expiration approaches. This is known as time erosion. “Theta” is a measure of how much time erosion affects the net price of a position. Long option positions have negative theta, which means they lose money from time erosion, if other factors remain constant; and short options have positive theta, which means they make money from time erosion.
A long butterfly spread with puts has a net positive theta as long as the stock price is in a range between the lowest and highest strike prices. If the stock price moves out of this range, however, the theta becomes negative as expiration approaches.
Risk of early assignment
Stock options in the United States can be exercised on any business day, and holders of short stock option positions have no control over when they will be required to fulfill the obligation. Therefore, the risk of early assignment is a real risk that must be considered when entering into positions involving short options.
While the long puts in a long butterfly spread have no risk of early assignment, the short puts do have such risk. Early assignment of stock options is generally related to dividends. Short puts that are assigned early are generally assigned on the ex-dividend date. In-the-money puts whose time value is less than the dividend have a high likelihood of being assigned.
If one short put is assigned, then 100 shares of stock are purchased and the long puts (lowest and highest strike prices) remain open. If a long stock position is not wanted, it can be closed in one of two ways. First, 100 shares can be sold in the marketplace. Second, the long 100-share position can be closed by exercising the higher-strike long put. Remember, however, that exercising a long put will forfeit the time value of that put. Therefore, it is generally preferable to sell shares to close the long stock position and then sell the long put. This two-part action recovers the time value of the long put. One caveat is commissions. Selling shares to close the long stock position and then selling the long put is only advantageous if the commissions are less than the time value of the long put.
If both of the short puts are assigned, then 200 shares of stock are purchased and the long puts (lowest and highest strike prices) remain open. Again, if a long stock position is not wanted, it can be closed in one of two ways. Either 200 shares can be sold in the marketplace, or both long puts can be exercised. However, as discussed above, since exercising a long put forfeits the time value, it is generally preferable to sell shares to close the long stock position and then sell the long puts. The caveat, as mentioned above, is commissions. Selling shares to close the long stock position and then selling the long puts is only advantageous if the commissions are less than the time value of the long puts.
Note, however, that whichever method is used, selling stock or exercising a long put, the date of the stock sale will be one day later than the date of the purchase. This difference will result in additional fees, including interest charges and commissions. Assignment of a short option might also trigger a margin call if there is not sufficient account equity to support the stock position created.
Potential position created at expiration
The position at expiration of a long butterfly spread with puts depends on the relationship of the stock price to the strike prices of the spread. If the stock price is above the highest strike price, then all puts expire worthless, and no position is created.
If the stock price is below the highest strike and at or above the center strike, then the highest strike long put is exercised. The result is that 100 shares of stock are sold short and a stock position of short 100 shares is created.
If the stock price is below the center strike and at or above the lowest strike, then the highest-strike long put is exercised and the two center-strike short puts are assigned. The result is that 100 shares are sold short and 200 shares are purchased. The net result is a long position of 100 shares.
If the stock price is below the lowest strike, then both long puts (highest and lowest strikes) are exercised and the two short puts (center strike) are assigned. The result is that 200 shares are sold short and 200 shares are purchased. The net result is no position, although several stock buy and sell commissions have been incurred.
Other considerations
A long butterfly spread with puts can also be described as the combination of a bear put spread and a bull put spread. The bear put spread is the long highest-strike put combined with one of the short center-strike puts, and the bull put spread is the other short center-strike put combined with the long lowest-strike put.
The term “butterfly” in the strategy name is thought to have originated from the profit-loss diagram. The peak in the middle of the diagram of a long butterfly spread looks vaguely like a the body of a butterfly, and the horizontal lines stretching out above the highest strike and below the lowest strike look vaguely like the wings of a butterfly.

