- Disability and life insurance
- Health insurance
- Dental and other insurance
- Business insurance
Disability and life insurance for self-employed
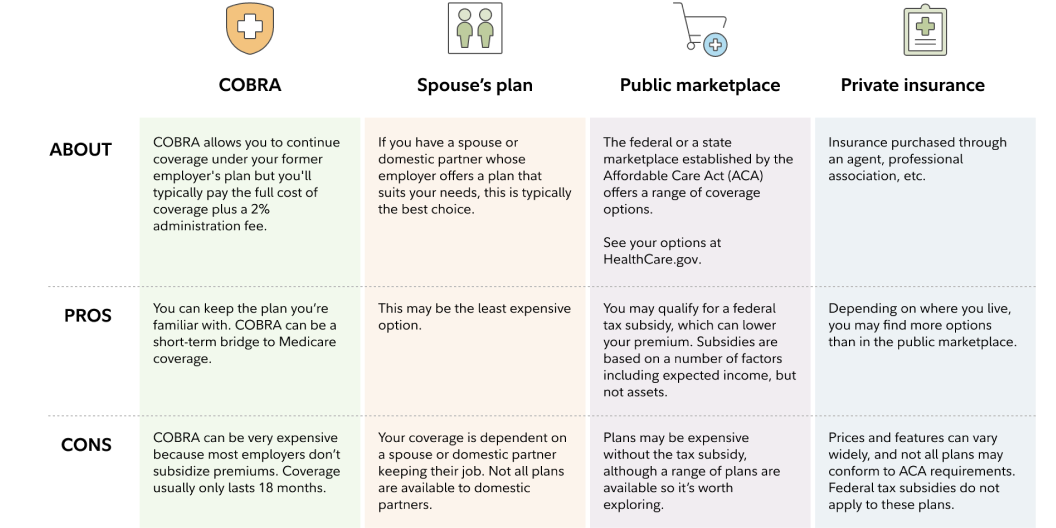
Health insurance for self-employed
Dental and other insurance for self-employed
Business insurance for self-employed
- General liability
- Product liability
- Professional liability
- Commercial property
- Home-based business
- Business owners’ policy


