If you are age 731 or older, IRS rules require you to take required minimum distributions (RMDs) each year from your tax-deferred retirement accounts.
A QCD is a direct transfer of funds from your IRA, payable directly to a qualified charity, as described in the QCD provision in the Internal Revenue Code. Amounts distributed as a QCD can be counted toward satisfying your RMD for the year, up to $108,000 in 2025 and $111,000 in 2026. The QCD is excluded from your taxable income. This is not the case with a regular withdrawal from an IRA, even if you use the money to make a charitable contribution later on. If you take a withdrawal, the funds would be counted as taxable income even if you later offset that income with the charitable contribution deduction.
Why is this distinction important? If you take the RMD as income, instead of as a QCD, your RMD will count as taxable income. This additional taxable income may push you into a higher tax bracket and may also reduce your eligibility for certain tax credits and deductions. To eliminate or reduce the impact of RMD income, charitably inclined investors may want to consider making a qualified charitable distribution (QCD). For example, your taxable income helps determine the amount of your Social Security benefits that are subject to taxes. Keeping your taxable income level lower may also help reduce your potential exposure to the Medicare surtax.
The rules of QCDs
A QCD must adhere to the following requirements:
|
Tax filing for QCDs
A QCD is reported by your IRA custodian as a normal distribution on IRS Form 1099-R for any non-Inherited IRAs. For Inherited IRAs or Inherited Roth IRAs, the QCD will be reported as a death distribution. You should keep an acknowledgement of the donation from the charity for your tax records. Please consult a tax advisor to learn more.
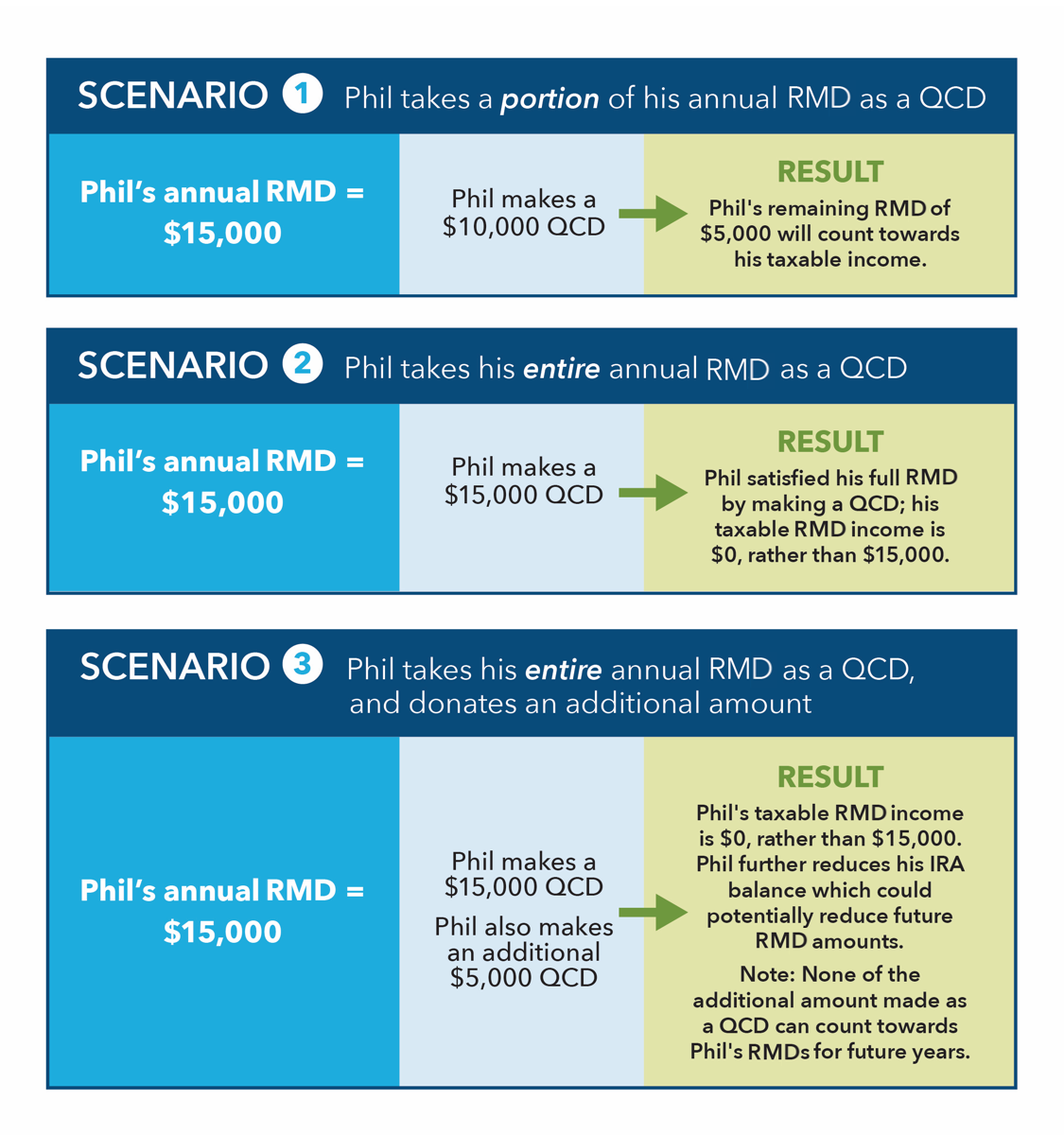
For a better understanding of how QCDs can affect your taxable income, let's consider a few hypothetical scenarios. Phil has been taking RMDs for the past few years, but this year he has decided to make a QCD. Phil did not make any non-deductible contributions to his IRA, so all of his distributions would be taxable:
If you are 70½, own an IRA, and donate to charity, QCDs may make sense for you; consult a tax advisor regarding your specific situation.


