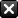How SARs work
Follow the journey of a typical award.

Accept your award.

Wait for your award to vest.

Exercise your rights before they expire and pay taxes.

The payout is now yours.
Let Fidelity help you plan.
Receiving stock appreciation rights (SARs) from your company is a big deal—congratulations! SARs are a form of equity compensation that give you the ability to receive shares or cash equal in value to the appreciation of company stock over a set period of time. In other words, if the stock price goes up between the grant date and the vesting date, you can exercise the rights for a payout of shares or cash.
Accepting your award and opening your account
To accept the award and make it officially yours, go to Fidelity NetBenefits®, where you can view your award details and estimate your payout. If you're new to Fidelity, you'll be asked to create a username and password and then open a Fidelity brokerage account (the Fidelity Account®) when you accept your award. If you already have an eligible account with us, we'll link your award to that account.
Tracking your award value
The value of your award is based on any increase in the share price of your company's stock over a set period. To see how much your award could be worth, go to NetBenefits.
Receiving your payout
After a waiting period that your company sets, your award vests and you can exercise the rights for shares or cash. Go to NetBenefits to find out when that happens.
Exercising stock appreciation rights
When the market price of the shares is higher than your grant price, your stock appreciation rights are "in the money." (If the market price is lower than the grant price, the rights are "underwater" or "out of the money" and you are unable to exercise them.) Once vested, you can exercise the rights to benefit from any stock price increase. Remember that your stock appreciation rights will expire, so be sure to exercise them in time.
Managing your payout
When you exercise your stock appreciation rights, the shares or cash will pay out to your brokerage account. You'll need this account to exercise your stock appreciation rights. To protect your assets, consider adding a beneficiary to your account. Easily sell some or all of your shares and link your bank account to access cash.
Understanding your taxes
Your award is considered taxable income when you exercise the rights. Your company may withhold the income taxes from your payout. If your award pays out as shares that you sell at a later point, you may also be subject to capital gains taxes. Use Fidelity's tax-planning resources to learn more about taxes, when they're paid, and how to file your tax return.
Getting help
We'll stay in touch through the full life cycle of your award and let you know when there's action to take. Head to your Profile page to confirm your contact information is correct, so you never miss an update or time-sensitive communications.
This video describes how stock options, which are very similar to stock appreciation rights, work.
Your Stock Plan Resource Center
The Stock Plan Resource Center provides the help and education you need to understand how your equity compensation works, including taxes, selling and managing shares, and planning for your financial goals and priorities.